LECTURE NO. 1 BY ENGR RAHAT ULLAH
BRICK MASONRY
PART 1
TYPES OF BRICKS:
- Bricks are made in a range of varieties, each intended for a specific purpose.
- Created from some combination of sand, water, clay, and heat.
- Building brick, or common brick, is used in construction and is provided with frog, which reduce weight of brick and increase strength.
- Face brick is chosen for visible surfaces or exposed walls and comes in different colors, sizes, and shapes.
- Firebrick is made with special clay to offer additional heat resistance in fireplaces or boiler rooms.
- Glazed brick is coated on one surface with a ceramic finish that is sanitary and easy to clean, making it popular in hospitals and laboratories.
TERMINOLOGY OF BRICKS:
Back
The inner surface of a wall which is not
exposed is called the back. The material forming the back is known as backing.
Face:
The exterior of wall exposed to weather
is known as face. The material used in the face of the wall is known as facing.
Hearting:
It
is the interior portion of a wall between the facing and backing.
Joint:
It
is the junction of two or more bricks or stones. If the joint is parallel to
the bed of bricks or stones in a course
then it is termed as bed joint. The joint which are perpendicular to the bed
joints are termed as vertical joints or side joints or perpends.
Bat:
it is the portion of brick cut across the
width.
Closer:
it is the portion of the brick cut length
wise in such a manner that its one long face remains uncut.
King Closer:
these are the portions of a brick obtained by
cutting off the triangular piece between
the center of one end and the center of one side.
Bevelled Closer:
it is that portion of a brick in which
the whole length of the brick is beveled for maintaining half width.
King closer
Bevelled closer
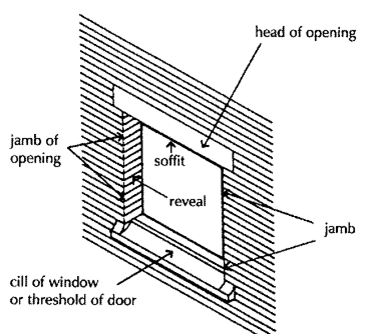
Jambs:
these
are the vertical sides of an opening for doors and windows. These may be plain
or splayed or may be provided with recesses to receive the frames of doors and
windows.
Reveals:
These are exposed vertical surfaces left
on the sides of an opening after the door or window frame had been fitted in
position.
sill level:
it is the level of the window from the
base (floor) ,through which a section is cut to show the plan of the structure.
Course:
A course is a horizontal layer of bricks
or stones.
Stretcher:
A masonry unit laid with its greatest
dimension horizontal and its face
parallel to the wall and a course having all
the bricks laid in stretcher is called a stretcher course.
Header:
a masonry unit laid with its small
dimension and parallel to the face of the masonry wall. A course having all the
bricks laid header wise is called header course.
Queen Closer:
A brick cut lengthwise in 9’’x2¼’’ is
called a queen closer and is placed next to the header course to break the
joints.
POINTING:
Tooling:
compressing and shaping the face of a mortar joint with a special tool other
than a trowel.
Tuck pointing:
filling in with fresh mortar of cutout or defective mortar joint in masonry.


 7:50 pm
7:50 pm
 Unknown
Unknown











 Posted in:
Posted in: 







0 comments:
Post a Comment